How to Generate a Token
In this section, we will see how OAuth is used to generate a token.
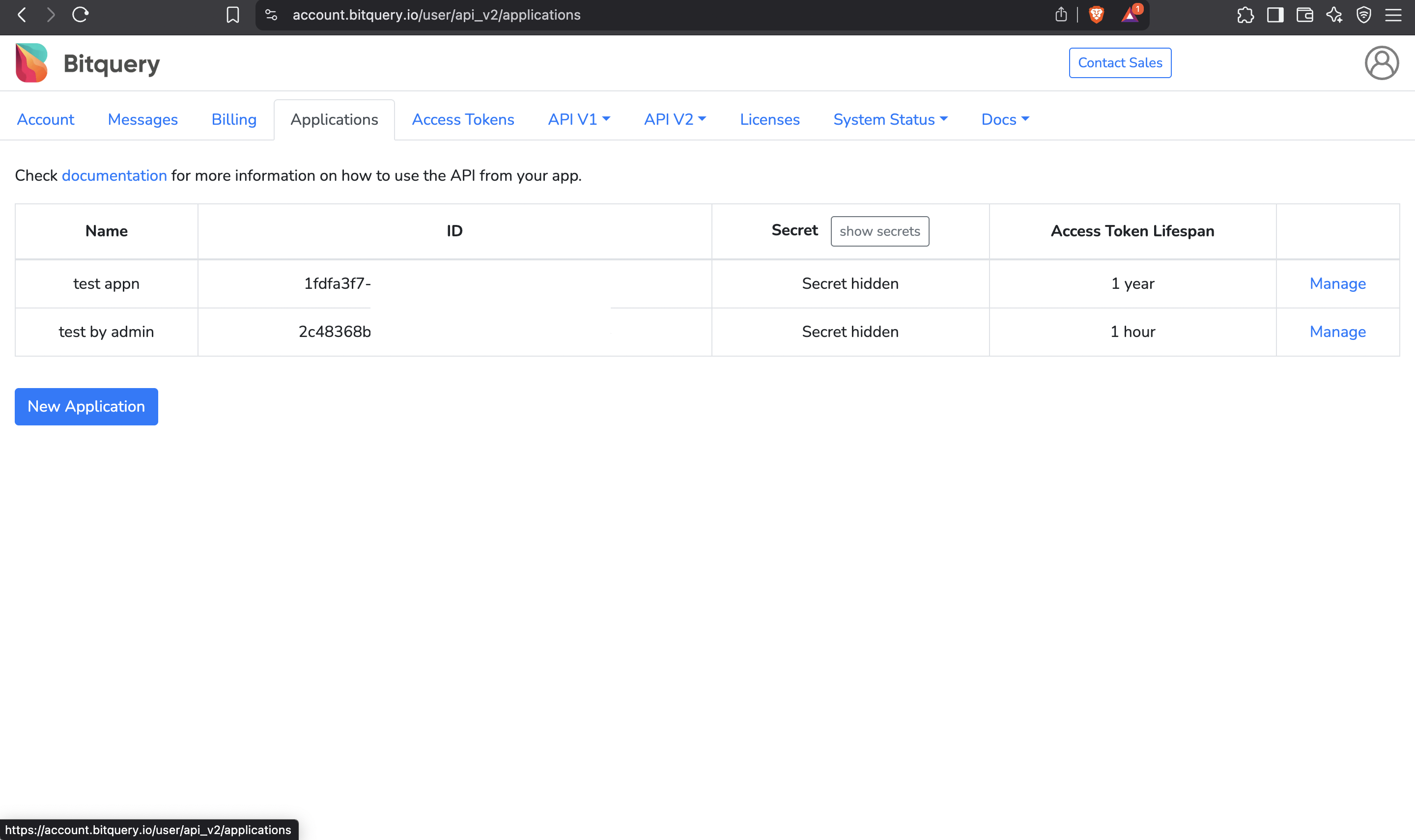
The first step is to create an application:
- Create an Application: Navigate to the Applications page and click
Create application. Enter a name for your application and select an expiration time for the access tokens. ClickCreate.
- Generate Access Token: We provide two methods to generate a token:
- You can generate a token for your application with a set expiration time.
- Or you can use your client ID-secret from your application to make a POST request to https://oauth2.bitquery.io/oauth2/token and get a token programmatically.
If you have no applications created, the
Bearertoken changes every 12 hours. If the token is invalid, you get "Unauthorized" message.
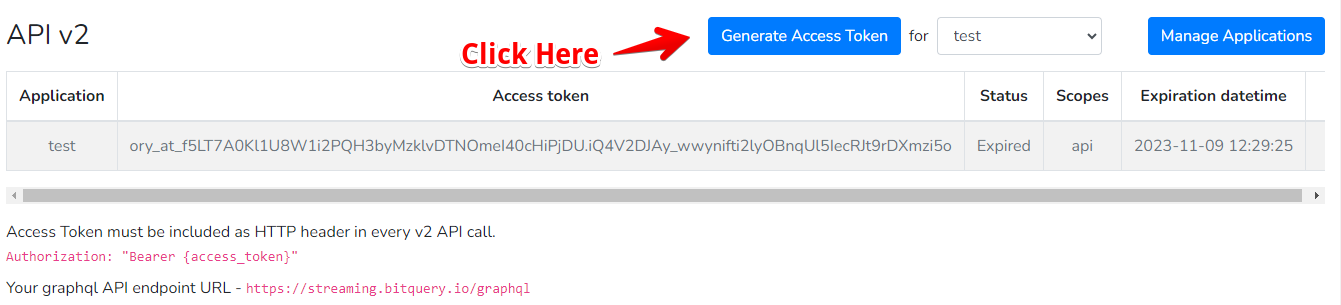
Generating a Token with Set Expiration Time
-
Go to the Access Token page and select the application for which you want to generate an access token.
-
Click Generate Access Token.
-
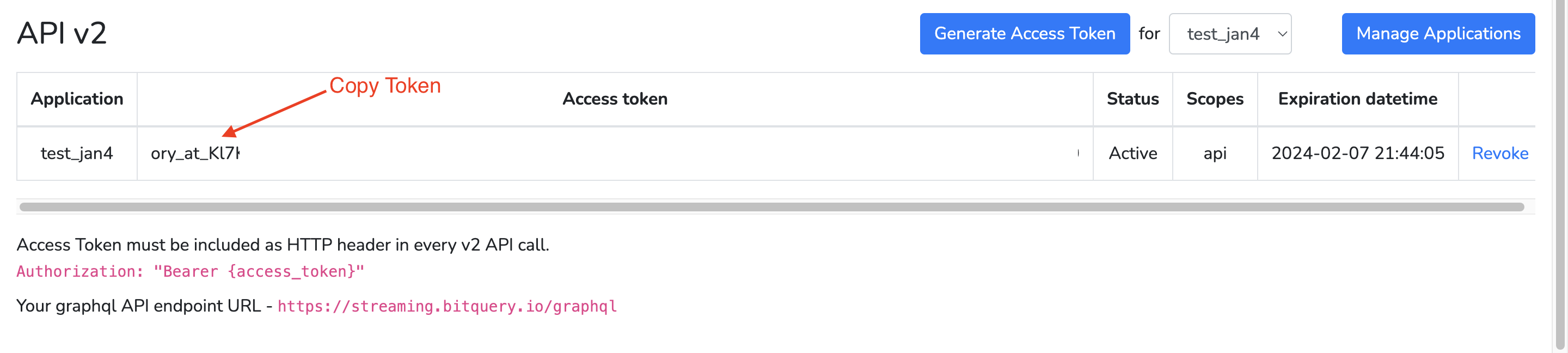
Copy the access token and store it in a secure location.
Using the token:
To utilize the token you've copied from the api_v2/access_tokens page, use the code generation feature on your IDE to obtain the code in your preferred programming language. However, remember to paste the token you've copied from the api_v2/access_tokens page. This is necessary because the IDE code generator only displays temporary tokens.
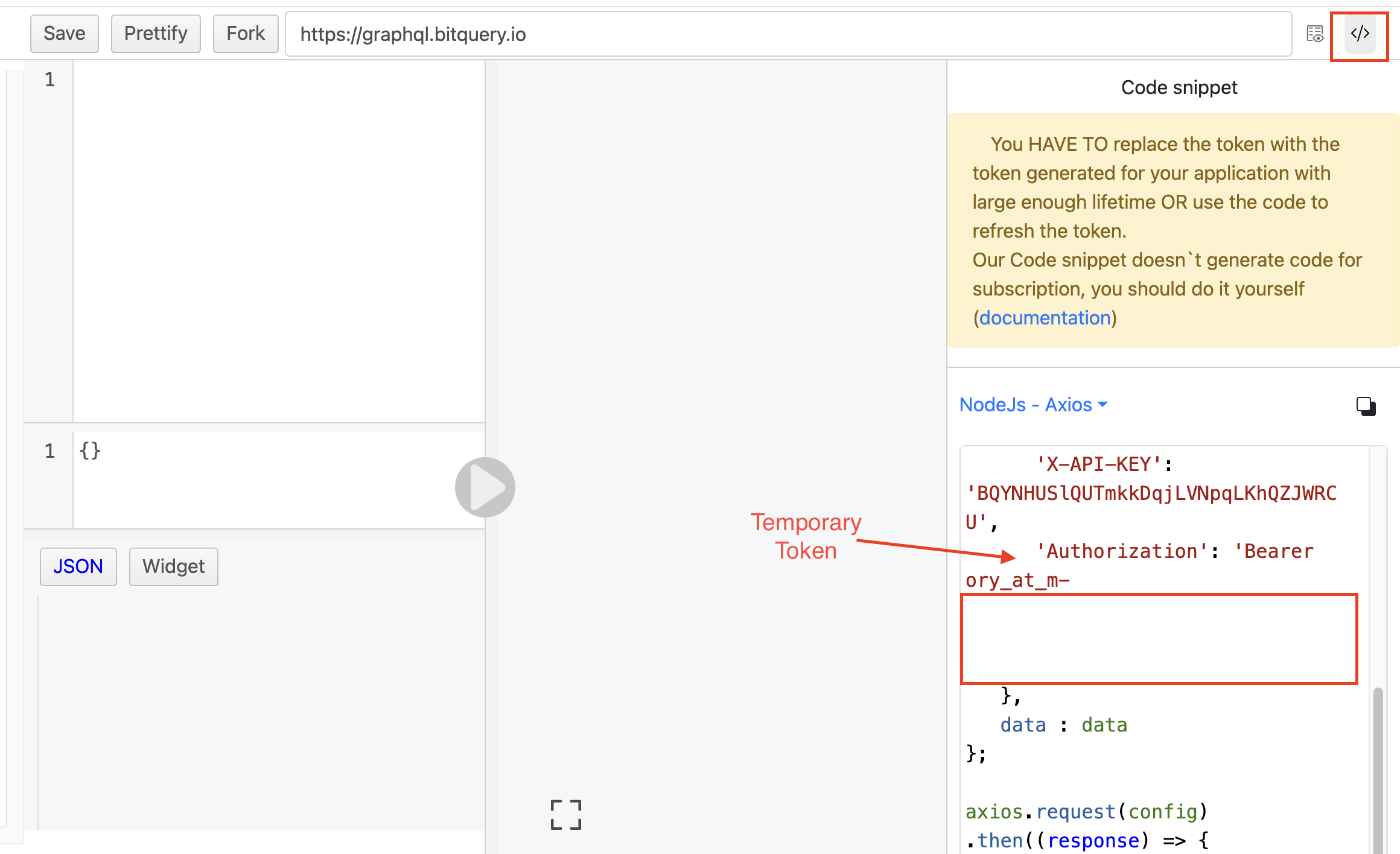
For example, you can include the token in the header as shown below:
Authorization: Bearer <access_token>
Refer Postman examples here
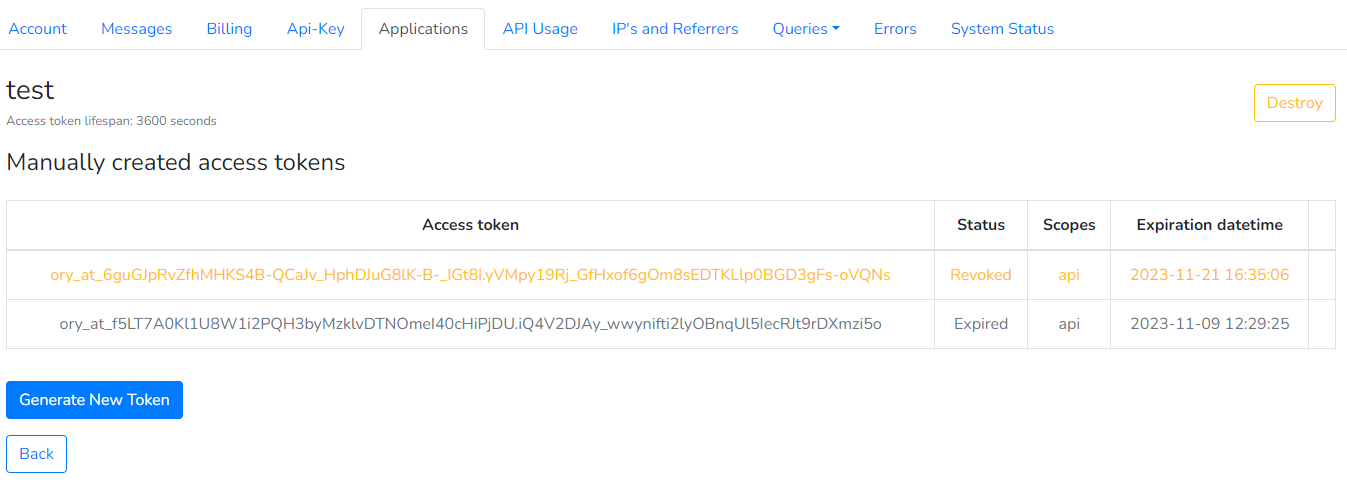
Revoking an Access Token
If you believe that your access token has been compromised, you can revoke it by clicking Revoke on the Applications page.
Generating a Token Programmatically
Remember that this approach requires more effort to implement. It is suitable for applications with a high risk of token theft or misuse. This approach expects you to programmatically generate an access token using your client ID and client secret of an application.
Below is a code snippet in Python that shows you how to programmatically generate a token and use the API, replace the placeholders with actual information.
Ensure that scope=api is mentioned in the payload,
import requests
import json
def oAuth_example():
url = "https://oauth2.bitquery.io/oauth2/token"
payload = 'grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=YOUR_ID_HERE&client_secret=YOUR_SECRET_HERE&scope=api'
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
response = requests.request("POST", url, headers=headers, data=payload)
resp = json.loads(response.text)
print(resp)
access_token=resp['access_token']
url_graphql = "https://streaming.bitquery.io/graphql"
headers_graphql = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'
}
//use the token to send a request
oAuth_example()
The response will include details on scope and expiration time of the token. A sample response looks like this:
{'access_token': 'ory_at_sKK8sSq8', 'expires_in': 2627999, 'scope': 'api', 'token_type': 'bearer'}
Deleting an Application
If you no longer need an application, you can delete it by clicking Delete on the Applications page. All the tokens associated with the application will no longer work.
Billing Considerations
- Billing remains consistent across API v1 and v2.
- Purchase points once and utilize them for either v1 or v2 in any combination.