Getting Ethereum Data from AWS Bucket
We are now offering raw blockchain data on Amazon S3, taking a step towards providing a faster way to build dApps.
Data on S3 uses the Protobuf schema that allows for more efficient data transfer and storage. To make things easier, I'll walk you through how to access the storage and parse the data in Python.
You can access the product on the AWS Marketplace here: https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/pp/prodview-oi4sbdu6zro3i
For this tutorial, we'll be using readily available sample datasets. So, let's get started!
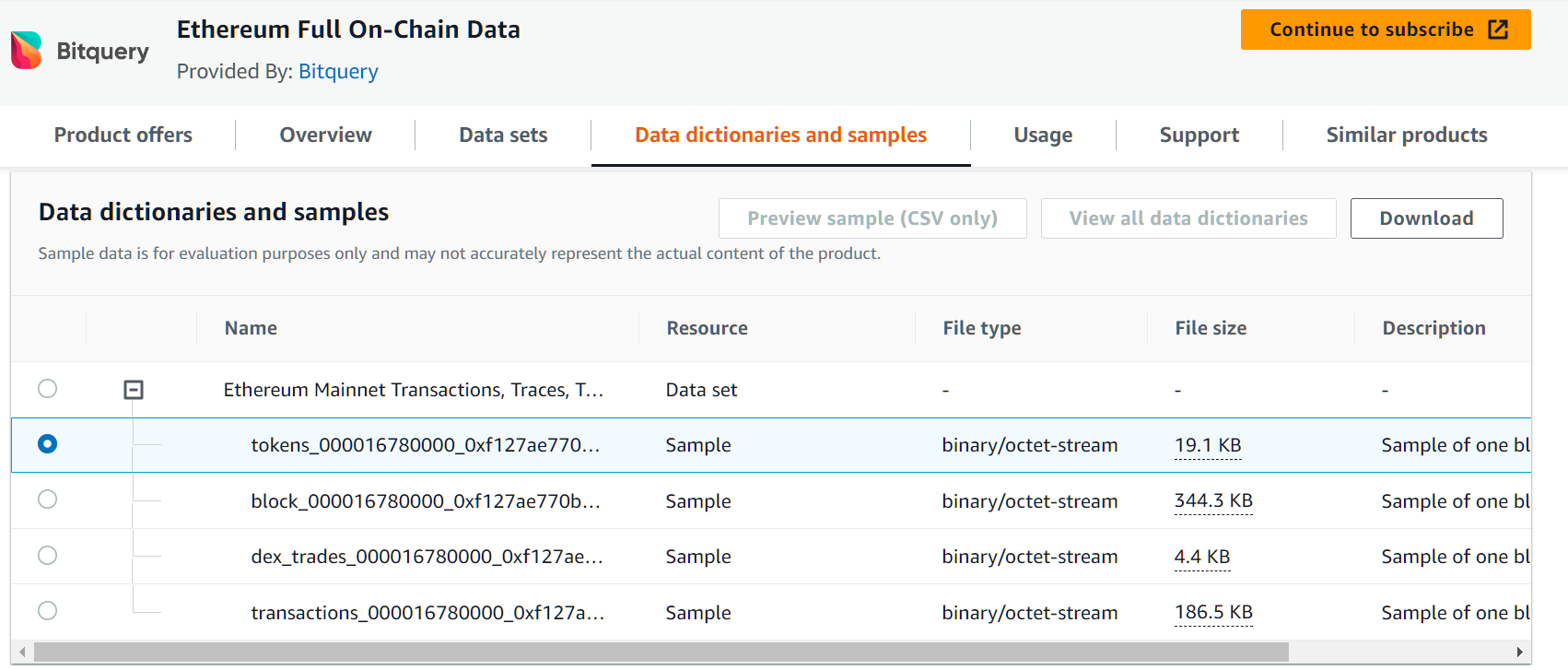
What does this code do?
This code performs the download and processing of two different files from an Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 bucket. Specifically, it downloads two files, decompresses them, and extracts information from them using Protocol Buffers.
You can access the complete Git repo here: https://github.com/bitquery/S3-Sample-Parse-Tutorial/tree/main
Step-by-Step Implemention
Import the necessary libraries
import boto3
import lz4.frame
import block_message_pb2
import json
from google.protobuf.json_format import MessageToJson
Access S3 bucket
For this step, you need to get your AWS Access Keys.
- Go to your AWS Console https://aws.amazon.com/console/
- Navigate to your profile -> Security credentials -> Generate Access Key
You can find the details of the demo buckets here https://github.com/bitquery/blockchain-cloud-data-dump-sample.git
The first part of the code uses the boto3 library to connect to the S3 bucket with the specified credentials. It then defines two object keys, block_object_key which correspond to the S3 object keys for the two files to be downloaded. It also specifies two local file paths, blocks_local_path and dextrades_local_path, which are where the downloaded files will be saved on the local system.
s3 = boto3.client('s3', aws_access_key_id='YOUR ID', aws_secret_access_key='YOUR KEY', region_name='us-east-1')
bucket_name = 'demo-streaming-eth'
block_object_key = 'eth.blocks.s3/000016780000/000016780000_0xf127ae770b9b73af1be93e5a7ac19be5e3bac41673b2685c6b4619fb09af09f0_41452bd33251301d32c606c704120d027de580505d611e4fb1c5ff3ef51d0cb7.block.lz4'
blocks_local_path = 'PATH TO YOUR FILE/s3downloadblocks.lz4'
Download the Files
In this step we use block_message_pb2 which are protobuf message files which contains the structure of the data.
We use the s3.download_file() method to download the file specified by block_object_key from the S3 bucket and save it to the local file path specified by blocks_local_path. The downloaded file is in a compressed format, so the code then uses the lz4.frame.decompress() method from the lz4 library to decompress the data.
s3.download_file(bucket_name, block_object_key, blocks_local_path)
with open(blocks_local_path, 'rb') as f:
compressed_data = f.read()
decompressed_data = lz4.frame.decompress(compressed_data)
print('here')
block_headers = block_message_pb2.BlockHeader()
block_headers.ParseFromString(decompressed_data)
print('here1')
Write to JSON files
The decompressed data is then parsed using the block_message_pb2.BlockHeader() method, which returns an object containing information about the block headers. The code then converts this object to a JSON string using the MessageToJson() method from the google.protobuf.json_format library and saves it to a file named block_headers.json.
# Write block_headers to a file
with open('block_headers.json', 'w') as f:
json_string = MessageToJson(block_headers)
f.write(json_string)