How to Write a Lambda Function to get Ethereum Data from AWS (Use AWS for Web3 )
In this tutorial we will see how to write a Lambda function to retrieve ethereum data from the sample buckets available in the AWS Marketplace.
Prerequisites
- An AWS account with appropriate permissions to create Lambda functions and S3 bucket access.
- Access to the Ethereum data in the specified S3 bucket
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Navigating to Lambda Functions Page
- Open your web browser and go to AWS Management Console.
- Sign in to your AWS account.
- Once signed in, navigate directly to the Lambda service by using the following URL: AWS Lambda Console
- Alternatively, you can access the Lambda console by following these steps:
- Click on "Services" in the top left corner of the AWS Management Console.
- In the "Compute" section, select "Lambda" from the options provided.
- Alternatively, you can access the Lambda console by following these steps:
Remember to replace region-name in the URL with the appropriate AWS region code where your Lambda functions are deployed. For example, us-east-1, us-west-2, etc. This will direct you to the Lambda console for the specified AWS region where you can manage your Lambda functions.
2. Prepare the Python Module as a Layer
The lz4 does not come preinstalled on the Python SDK in AWS .
To use the lz4 module in your Lambda function, you'll need to create a Python layer. Here's how you can do it:
Open a new terminal on your machine and run the following commands. This will create a zip file with the lz4
package installed
# Install lz4 to a local directory
pip3 install --target ./python lz4
# Create a ZIP archive of the Python module
zip -r lz4.zip ./python
Once done, go to the Lambda function page, scroll down to "Layers" in the Designer section.
- Click on "Add a layer" and select "Upload a .zip file".
- Upload the
lz4.zipfile you created earlier. - Add the layer to your Lambda function.
3. Create a Lambda Function
- Go to the AWS Lambda Console.
- Click on "Create function" and choose "Author from scratch".
- Give your function a name, choose Python 3.x as the runtime, and select an appropriate role with S3 read permissions.
- Click on "Create function".
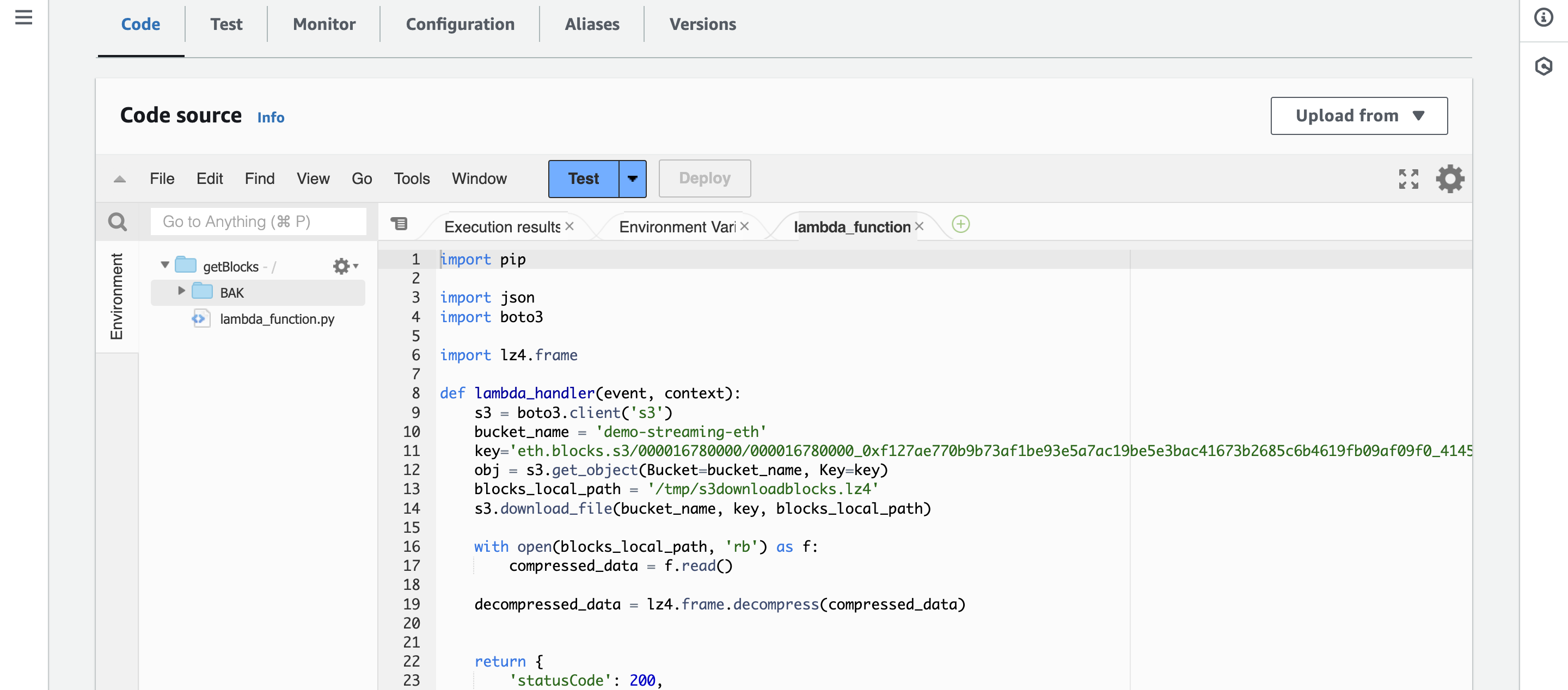
4. Configure the Lambda Function Code
Replace the default function code with the following Python code:
import json
import boto3
import lz4.frame
def lambda_handler(event, context):
s3 = boto3.client('s3')
bucket_name = 'demo-streaming-eth'
key = 'eth.blocks.s3/000016780000/000016780000_0xf127ae770b9b73af1be93e5a7ac19be5e3bac41673b2685c6b4619fb09af09f0_41452bd33251301d32c606c704120d027de580505d611e4fb1c5ff3ef51d0cb7.block.lz4'
obj = s3.get_object(Bucket=bucket_name, Key=key)
blocks_local_path = '/tmp/s3downloadblocks.lz4'
s3.download_file(bucket_name, key, blocks_local_path)
with open(blocks_local_path, 'rb') as f:
compressed_data = f.read()
decompressed_data = lz4.frame.decompress(compressed_data)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'File downloaded and processed successfully'
}
This code uses the boto3 library to download from the s3 bucket at eth.blocks.s3/000016780000/ and store it in s3downloadblocks.lz4 file. Once downloaded to local library on AWS, we use the lz4 module to decompress the data.
5. Configure Environment Variables (Optional)
If needed, you can set environment variables for the Lambda function to specify bucket names or keys dynamically.
6. Save and Test the Lambda Function
- Click on "Save" at the top right of the Lambda function editor.
- Use the "Test" button to simulate a test event. Ensure that the function executes without errors.
7. Invocation and Monitoring
- Once the function is properly configured, you can invoke it through the Lambda console or integrate it with other AWS services.
Remember to replace the bucket_name and key variables in the code with the appropriate S3 bucket details and Ethereum data file's key you want to retrieve. Adjust the code as needed to suit your specific use case.