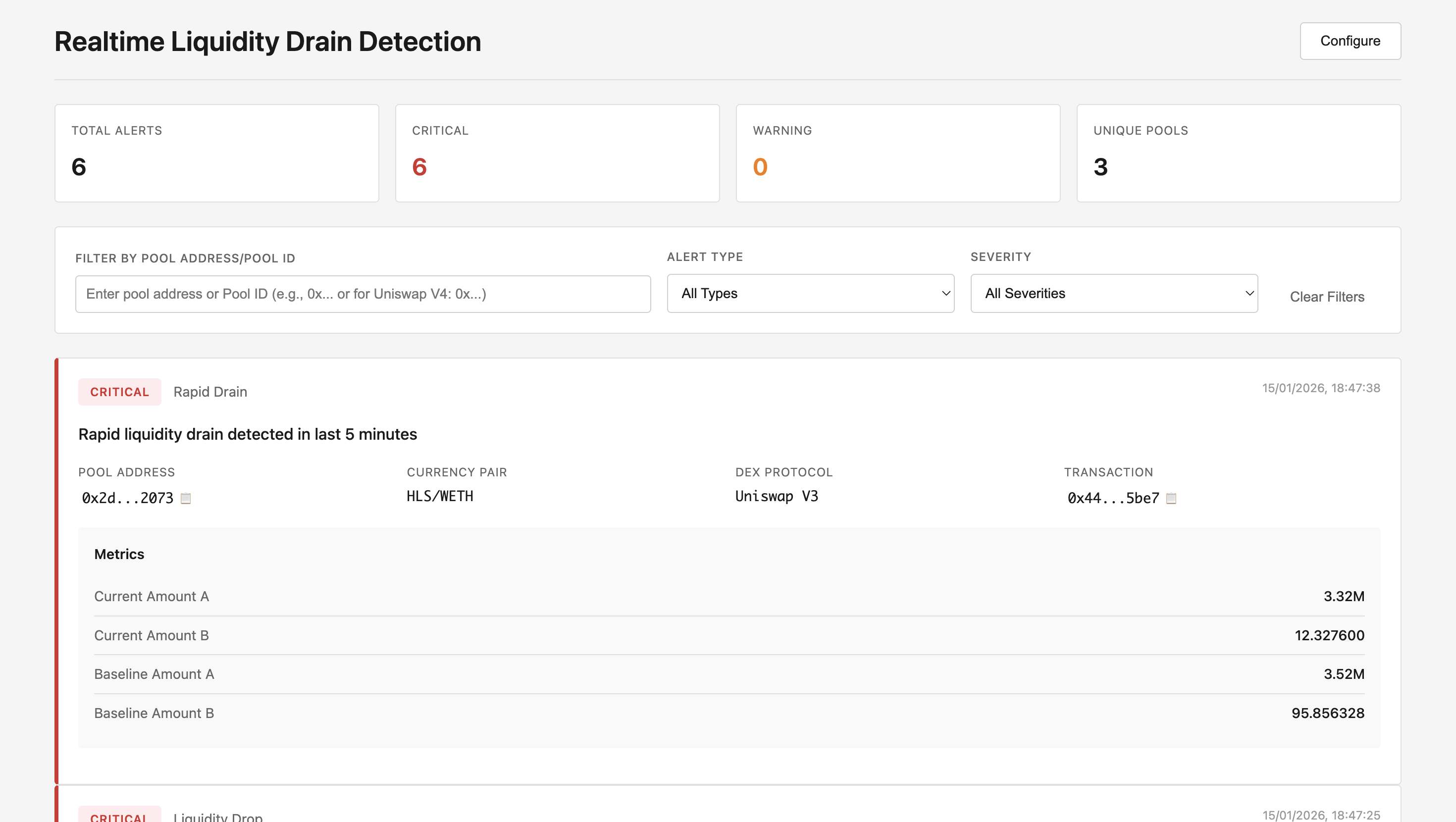
Realtime Liquidity Drain Detector
This guide demonstrates how to build a real-time DeFi security tool that monitors DEX pools to detect liquidity drains using Bitquery's Kafka streams. The tool provides instant alerts when significant liquidity drops are detected in DEX pools, helping protect against potential liquidity drains.
⚠️ Important: Proof of Concept
This tool is provided as a proof of concept for educational purposes. The detection logic may generate false positives and should be modified based on your requirements. Always verify alerts by checking on-chain transaction data before taking action.
GitHub Repository: realtime-liquidity-drain-detector
Overview
The Realtime Liquidity Drain Detector is a Python-based security tool that:
- Monitors DEX pools in real-time using Bitquery's Kafka streams
- Detects significant liquidity drops that may indicate malicious activity
- Provides a web dashboard for instant alerts and monitoring
- Configurable thresholds for warning and critical alerts
- Supports multiple DEX protocols including Uniswap V2, V3, and V4
Prerequisites
- Python 3.8+ installed on your system
- Bitquery Kafka Credentials - Contact sales via Telegram or fill out the form for Kafka access
- Bitquery API Token - Get your API token here
- Basic understanding of Kafka streams and Python
Note: IDE credentials will not work with Kafka Streams. You need separate Kafka credentials for this tool.
Installation
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Akshat-cs/realtime-liquidity-drain-detector
cd realtime-liquidity-drain-detector
- Install the required dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Configure your credentials:
- Copy
config.sample.pytoconfig.py:
cp config.sample.py config.py- Edit
config.pywith your Kafka credentials:
username = "your_kafka_username"
password = "your_kafka_password" - Copy
Configuration
Note: The default configuration values are starting points for a proof of concept. You should tune these parameters based on your specific requirements and testing to minimize false positives and optimize detection accuracy for your use case.
Edit thresholds in detection_config.py to customize alert sensitivity:
class DetectionConfig:
# Liquidity drop percentage thresholds
LIQUIDITY_DROP_WARNING = 20.0 # 20% drop = warning level alert
LIQUIDITY_DROP_CRITICAL = 40.0 # 40% drop = critical level alert
# Time windows
BASELINE_WINDOW_HOURS = 24 # Hours of data to build baseline
LOOKBACK_WINDOW_MINUTES = 30 # Minutes to check for recovery (false positive filter)
RAPID_DRAIN_WINDOW_MINUTES = 5 # Window for detecting sudden drains
# Max trade size decrease thresholds
MAX_AMOUNT_DECREASE_WARNING = 30.0 # 30% decrease = warning
MAX_AMOUNT_DECREASE_CRITICAL = 50.0 # 50% decrease = critical
# Alert management
ALERT_COOLDOWN_MINUTES = 10 # Minutes between alerts for same pool
RECOVERY_CHECK_ENABLED = True # Check if liquidity recovers quickly (false positive filter)
# False positive prevention
DROP_CONFIRMATION_COUNT = 2 # Number of consecutive measurements showing drop required before alerting
ENABLE_MAX_AMOUNT_DECREASE_ALERTS = False # Set to False to disable max_amount_decrease alerts
# Pool size filter
MIN_LIQUIDITY_TOKENS = 1000 # Minimum liquidity to monitor (filters out very small pools)
# Baseline reliability
MIN_MEASUREMENTS_FOR_BASELINE = 10 # Need at least 10 measurements before alerting
MIN_TIME_FOR_BASELINE_MINUTES = 5 # Need at least 5 minutes of data before alerting
Running the Tool
Start the API Server (Frontend Dashboard)
The API server provides a web dashboard for viewing alerts:
python api_server.py
Access the dashboard at: http://localhost:5001
Start the Detector
The detector monitors Kafka streams and sends alerts to the API server:
python liquidity_drain_detector.py
The detector will automatically send alerts to the API server when liquidity drains are detected.
How It Works
1. Real-Time Monitoring
The tool connects to Bitquery's Kafka streams for Ethereum DEX pools using the topic:
eth.dexpools.proto
The Kafka consumer is configured with:
conf = {
'bootstrap.servers': 'rpk0.bitquery.io:9092,rpk1.bitquery.io:9092,rpk2.bitquery.io:9092',
'group.id': f'{username}-liquidity-drain-{group_id_suffix}',
'session.timeout.ms': 30000,
'security.protocol': 'SASL_PLAINTEXT',
'ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm': 'none',
'sasl.mechanisms': 'SCRAM-SHA-512',
'sasl.username': config.username,
'sasl.password': config.password,
'auto.offset.reset': 'latest',
}
Kafka streams provide:
- Lower latency due to shorter data pipeline
- Better reliability with persistent connections
- Ability to read from latest offset without gaps
- Better scalability with multiple consumers
For detailed information on Kafka streams, refer to the Kafka Streaming Concepts documentation.
2. Data Structures
The tool uses three main data structures:
PoolState
Tracks the current state of a liquidity pool:
@dataclass
class PoolState:
pool_id: str
pool_address: str
currency_a: str
currency_b: str
currency_a_symbol: str
currency_b_symbol: str
dex_protocol: str
amount_a: float = 0.0 # Human-readable liquidity for currency A
amount_b: float = 0.0 # Human-readable liquidity for currency B
slippage_at_bps_a_to_b: Dict[int, Dict] # Slippage data for A->B swaps
slippage_at_bps_b_to_a: Dict[int, Dict] # Slippage data for B->A swaps
price_a_to_b: float = 0.0
price_b_to_a: float = 0.0
last_updated: datetime
PoolHistory
Maintains historical data for baseline calculation and drain detection:
@dataclass
class PoolHistory:
pool_id: str
amount_a_history: deque # Historical liquidity for currency A
amount_b_history: deque # Historical liquidity for currency B
max_amount_history_a_to_b_100bp: deque # Max trade size history (A->B at 100bp)
max_amount_history_b_to_a_100bp: deque # Max trade size history (B->A at 100bp)
baseline_amount_a: Optional[float] # Baseline liquidity for currency A
baseline_amount_b: Optional[float] # Baseline liquidity for currency B
baseline_max_amount_a_to_b_100bp: Optional[float]
baseline_max_amount_b_to_a_100bp: Optional[float]
recent_drop_measurements_a: deque # Track recent drops for confirmation
recent_drop_measurements_b: deque
3. Liquidity Drain Detection
The detector processes pool events from Kafka and performs three types of checks:
A. Liquidity Drop Detection
Tracks each currency separately and detects drops from baseline:
def _check_liquidity_drop(self, state: PoolState, history: PoolHistory,
current_amount_a: float, current_amount_b: float,
current_time: datetime) -> List[DrainAlert]:
# Calculate drop percentage for each currency
drop_a, drop_b = history.amount_drop_percent(current_amount_a, current_amount_b)
# Pre-alert confirmation: Require multiple consecutive measurements
if len(history.recent_drop_measurements_a) >= DROP_CONFIRMATION_COUNT:
if drop_a >= LIQUIDITY_DROP_CRITICAL:
severity = 'critical'
elif drop_a >= LIQUIDITY_DROP_WARNING:
severity = 'warning'
# Generate alert...
Key Features:
- Tracks each currency (A and B) separately
- Requires
DROP_CONFIRMATION_COUNTconsecutive measurements showing drop - Uses mean of last 24 hours as baseline
- Checks for recovery to filter false positives
B. Max Amount Decrease Detection
Monitors when maximum trade sizes decrease significantly:
def _check_max_amount_decrease(self, state: PoolState, history: PoolHistory,
max_amount_a_to_b: Optional[float],
max_amount_b_to_a: Optional[float],
current_time: datetime) -> List[DrainAlert]:
# Check both swap directions
decrease_a = history.max_amount_decrease_percent(max_amount_a_to_b, 'a_to_b')
decrease_b = history.max_amount_decrease_percent(max_amount_b_to_a, 'b_to_a')
# Use worst-case direction
if worst_decrease >= 50.0:
severity = 'critical'
elif worst_decrease >= 30.0:
severity = 'warning'
Note: This alert type is disabled by default (ENABLE_MAX_AMOUNT_DECREASE_ALERTS = False) as it can cause false positives.
C. Rapid Drain Detection
Detects sudden drops within a short time window:
def _check_rapid_drain(self, state: PoolState, history: PoolHistory,
current_amount_a: float, current_amount_b: float,
current_time: datetime) -> List[DrainAlert]:
# Check if liquidity dropped rapidly within RAPID_DRAIN_WINDOW_MINUTES
if history.is_rapid_drain(current_amount_a, current_amount_b, current_time):
# Generate critical alert...
4. Baseline Calculation
The baseline is calculated using the mean of measurements from the last 24 hours:
def update_baseline(self, current_time: datetime):
cutoff_time = current_time - timedelta(hours=BASELINE_WINDOW_HOURS)
# Baseline for currency A (mean - better for gradual drain detection)
recent_amount_a = [amt for ts, amt in self.amount_a_history
if ts >= cutoff_time and amt > 0]
if recent_amount_a:
self.baseline_amount_a = sum(recent_amount_a) / len(recent_amount_a)
Baseline Requirements:
- Minimum 10 measurements (
MIN_MEASUREMENTS_FOR_BASELINE) - Minimum 5 minutes of data (
MIN_TIME_FOR_BASELINE_MINUTES) - Uses mean (not max) for better sensitivity to gradual drains
5. Alert Generation
When a liquidity drain is detected, the tool generates a comprehensive alert including:
- Alert Type:
liquidity_drop,max_amount_decrease, orrapid_drain - Severity: Warning or Critical
- Pool Information: Pool ID, address, token pair, DEX protocol
- Transaction Details: Transaction hash and timestamp
- Liquidity Metrics: Current vs baseline liquidity for both tokens
- Slippage Data: Max trade sizes at different slippage levels (10bp, 50bp, 100bp, 200bp, 500bp, 1000bp)
- Drop Percentages: Detailed breakdown of liquidity drops
Sample Alert Output
================================================================================
🚨 LIQUIDITY DRAIN ALERT - CRITICAL
================================================================================
Type: liquidity_drop
Pool ID: 0x10bd2f65f40bc8b7ddb6f104c603d022cd8a0ddf_0xc02aaa39b223fe8d0a0e5c4f27ead9083c756cc2_0xdd9f7920b7c77efa8d1c19e3a7c1151f985f75a6
Pool Address: 0x10bd2f65f40bc8b7ddb6f104c603d022cd8a0ddf
Pair: WETH/ASTRE
DEX: uniswap_v2
Transaction Hash: 0x73470ed71e7b251d0e94078559d3c9005dc14187f55b61ad9435e99feb2341ea
Time: 2026-01-15 13:17:25 UTC
ASTRE dropped 90.4% from baseline
Current State:
Currency A: WETH (0xc02aaa39b223fe8d0a0e5c4f27ead9083c756cc2)
- Current Liquidity: 0.000000 WETH
- Baseline Liquidity: 1.300800 WETH
- Drop: +100.0%
Currency B: ASTRE (0xdd9f7920b7c77efa8d1c19e3a7c1151f985f75a6)
- Current Liquidity: 15,357,735,936.000000 ASTRE
- Baseline Liquidity: 159,272,254,854.947357 ASTRE
- Drop: +90.4%
A->B MaxAmountIn (all slippage levels):
(10bp): Baseline: 0.000654 WETH, Drop: +100.0%
(50bp): Baseline: 0.003282 WETH, Drop: +100.0%
(100bp): Baseline: 0.006592 WETH, Drop: +100.0%
(200bp): Baseline: 0.013285 WETH, Drop: +100.0%
(500bp): Baseline: 0.034013 WETH, Drop: +100.0%
(1000bp): Baseline: 0.070822 WETH, Drop: +100.0%
B->A MaxAmountIn (all slippage levels):
(10bp): Baseline: 80,055,434.984426 ASTRE, Drop: +90.4%
(50bp): Baseline: 399,877,993.949424 ASTRE, Drop: +90.4%
(100bp): Baseline: 799,081,216.317845 ASTRE, Drop: +90.4%
(200bp): Baseline: 1,594,216,258.495066 ASTRE, Drop: +90.4%
(500bp): Baseline: 3,958,883,536.978619 ASTRE, Drop: +90.4%
(1000bp): Baseline: 7,824,577,583.154605 ASTRE, Drop: +90.4%
History Stats:
- Liquidity A measurements: 19
- Liquidity B measurements: 19
- MaxAmountIn measurements: 19
- Baseline window: Last 24 hours
⚠️ VALIDATION NOTES:
- For Uniswap V4: Liquidity amounts are AGGREGATED across all pools
- MaxAmountIn is POOL-SPECIFIC (drops reflect this specific pool's drain)
- Baseline uses last 24 hours of data
- Check transaction hash on Etherscan to verify on-chain events
================================================================================
Project Structure
The project consists of three main files:
-
liquidity_drain_detector.py(1052 lines): Main detector logic- Data structures (
PoolState,PoolHistory,DrainAlert) - Detection engine (
LiquidityDrainDetectorclass) - Kafka consumer integration
- Alert formatting and API communication
- Data structures (
-
detection_config.py(55 lines): Configuration class- All detection thresholds and parameters
- Time windows and filtering options
- Baseline requirements
-
api_server.py(345 lines): Flask API server- REST API endpoints for alerts
- Frontend dashboard serving
- Alert storage and filtering
- Configuration management
Code Walkthrough
Main Execution Flow
The main function sets up the Kafka consumer and processes messages:
def main():
# Setup logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
# Initialize detector
detector = LiquidityDrainDetector()
# Configure Kafka consumer
conf = {
'bootstrap.servers': 'rpk0.bitquery.io:9092,rpk1.bitquery.io:9092,rpk2.bitquery.io:9092',
'group.id': f'{config.username}-liquidity-drain-{group_id_suffix}',
'security.protocol': 'SASL_PLAINTEXT',
'sasl.mechanisms': 'SCRAM-SHA-512',
'sasl.username': config.username,
'sasl.password': config.password,
'auto.offset.reset': 'latest',
}
consumer = Consumer(conf)
consumer.subscribe(['eth.dexpools.proto'])
# Main processing loop
while True:
msg = consumer.poll(timeout=1.0)
if msg is None:
continue
# Parse protobuf message
dex_pool_block = dex_pool_block_message_pb2.DexPoolBlockMessage()
dex_pool_block.ParseFromString(msg.value())
# Process each pool event
for pool_event in dex_pool_block.PoolEvents:
alerts = detector.process_pool_update(pool_event)
# Handle alerts
for alert in alerts:
print(format_alert(alert, state, history))
send_alert_to_api(alert, api_url, logger)
Processing Pool Updates
The process_pool_update method handles each pool event:
def process_pool_update(self, dex_pool_event) -> List[DrainAlert]:
# Extract pool information
pool = dex_pool_event.Pool
liquidity = dex_pool_event.Liquidity
price_table = dex_pool_event.PoolPriceTable
# For Uniswap V4, use PoolId; for others, use composite key
if protocol_name == 'uniswap_v4':
pool_id = convert_bytes_to_hex(pool.PoolId).lower()
else:
pool_id = f"{pool_address}_{currency_a}_{currency_b}"
# Update pool state with current liquidity and slippage data
state.amount_a = liquidity.AmountCurrencyA # Already human-readable
state.amount_b = liquidity.AmountCurrencyB # Already human-readable
# Process slippage data at multiple levels (10bp, 50bp, 100bp, etc.)
for price_info in price_table.AtoBPrices:
bps = price_info.SlippageBasisPoints
max_in = price_info.MaxAmountIn # Already human-readable
state.slippage_at_bps_a_to_b[bps] = {
'max_amount_in': max_in,
'min_amount_out': price_info.MinAmountOut,
'price': price_info.Price
}
# Add measurement to history
history.add_measurement(amount_a_human, amount_b_human,
max_amount_a_to_b_100bp, max_amount_b_to_a_100bp,
max_amounts_a_to_b_all, max_amounts_b_to_a_all,
current_time)
# Run detection checks if baseline is sufficient
if history.has_sufficient_baseline(current_time):
alerts.extend(self._check_liquidity_drop(...))
alerts.extend(self._check_max_amount_decrease(...))
alerts.extend(self._check_rapid_drain(...))
API Server Endpoints
The Flask API server provides several endpoints for the web dashboard:
Get Alerts
GET /api/alerts?pool=<pool_address>&type=<alert_type>&severity=<severity>&limit=<number>
Returns filtered list of alerts. Filters:
pool: Filter by pool address or pool ID (case-insensitive)type: Filter by alert type (liquidity_drop,max_amount_decrease,rapid_drain)severity: Filter by severity (warning,critical)limit: Maximum number of alerts to return (default: 100)
Response:
{
"alerts": [...],
"total": 10,
"total_all": 50
}
Get Alert Statistics
GET /api/alerts/stats
Returns statistics about all alerts:
{
"total_alerts": 50,
"by_severity": {"critical": 20, "warning": 30},
"by_type": {"liquidity_drop": 45, "rapid_drain": 5},
"by_dex": {"uniswap_v2": 30, "uniswap_v3": 20},
"unique_pools": 15
}
Get Configuration
GET /api/config
Returns current detection thresholds:
{
"liquidity_drop_warning": 20.0,
"liquidity_drop_critical": 40.0,
"max_amount_decrease_warning": 30.0,
"max_amount_decrease_critical": 50.0,
"rapid_drain_threshold": 20.0
}
Update Configuration
POST /api/config
Content-Type: application/json
{
"liquidity_drop_warning": 25.0,
"liquidity_drop_critical": 45.0
}
Updates detection thresholds (validates values are between 0-100).
Add Alert (Internal)
POST /api/alerts
Content-Type: application/json
{
"pool_id": "0x...",
"severity": "critical",
"alert_type": "liquidity_drop",
"message": "WETH dropped 90.4% from baseline",
"timestamp": "2026-01-15T13:17:25Z",
"pool_info": {
"pool_id": "...",
"pool_address": "0x...",
"currency_pair": "WETH/ASTRE",
"dex": "uniswap_v2",
"transaction_hash": "0x..."
},
"metrics": {...}
}
Called by the detector to add new alerts. Alerts are stored in memory (max 1000, or 24 hours retention).
Get Pools
GET /api/pools
Returns list of unique pools that have generated alerts:
{
"pools": [
{
"pool_id": "0x...",
"pool_address": "0x...",
"currency_pair": "WETH/ASTRE",
"dex": "uniswap_v2",
"alert_count": 5
}
],
"total": 15
}
Understanding the Data
Protobuf Message Structure
The tool processes DexPoolBlockMessage protobuf messages from Kafka, which contain:
- PoolEvents: Array of pool update events
- Pool: Pool information (address, PoolId, currencies, decimals)
- Liquidity: Current reserves (AmountCurrencyA, AmountCurrencyB) - already human-readable floats
- PoolPriceTable: Slippage and price data
- AtoBPrices: Array of price info for A→B swaps at different slippage levels
- BtoAPrices: Array of price info for B��→A swaps at different slippage levels
- Each price info contains: SlippageBasisPoints, MaxAmountIn, MinAmountOut, Price
- Dex: DEX protocol information (ProtocolName, SmartContract)
- TransactionHeader: Transaction hash (optional)
Pool Identification
The tool uses different pool identification strategies:
- Uniswap V4: Uses
PoolId(bytes converted to hex) since liquidity is aggregated in PoolManager - Other Protocols: Uses composite key:
{pool_address}_{currency_a}_{currency_b}(sorted)
Important Notes
- Uniswap V4: Liquidity amounts are aggregated across all pools in the PoolManager contract. Use
PoolIdto differentiate between pools. MaxAmountIn is pool-specific and will show drops. - Baseline Calculation: Uses the mean of measurements from the last 24 hours (not max) for better sensitivity to gradual drains
- Human-Readable Values: The protobuf schema now sends liquidity and slippage values as human-readable floats (no decimal conversion needed)
- Validation: Always verify alerts by checking the transaction hash on Etherscan
Use Cases
1. DeFi Security Monitoring
Monitor DEX pools for suspicious liquidity withdrawals that may indicate:
- Liquidity drain attacks
- Protocol exploits
- Market manipulation
2. Risk Management
Before executing large trades:
- Check current pool liquidity depth
- Verify sufficient liquidity exists for your trade size
- Monitor for recent liquidity drains that may affect execution
3. Trading Strategy Protection
- Avoid entering positions when liquidity is thin
- Detect when pools become less liquid
- Identify pools experiencing rapid liquidity growth or decline
4. Portfolio Protection
- Monitor pools for tokens in your portfolio
- Get alerts before liquidity drains affect token prices
- Track liquidity health across multiple pools
Related Documentation
- Kafka Streaming Concepts
- EVM Protobuf Kafka Streams
- Ethereum Liquidity API
- Ethereum Slippage API
- DEXPools Cube Documentation
Important Considerations
This tool is provided as a proof of concept and should be considered a starting point for building your own liquidity monitoring solution. The detection logic may generate false positives due to legitimate large trades, normal liquidity rebalancing, temporary market fluctuations, or legitimate protocol operations.
For production use, you should modify the detection logic, tune thresholds based on your specific use case, implement additional validation rules, and integrate with your existing monitoring infrastructure. This tool is not intended for production use without significant modifications, testing, and hardening.
Support
For issues or questions:
- Open an issue on GitHub
- Contact Bitquery support via Telegram
- Check the Bitquery Documentation