Get Blockchain Data on Telegram Chat in Real-Time
With this code, your Telegram bot will respond to the /start command by initiating a WebSocket connection to Bitquery and sending blockchain data updates to the Telegram chat.
This is how it will look 
You can find the complete code here
Step-by-Step Tutorial
- Install the required Python libraries:
pip install asyncio json websockets tracemalloc telegram-bot-api
Step 2: Define Your Token and Keys You need to provide your Telegram bot token from the BotFather. For this step you need to create a new Telegram bot. Check official tutorial here
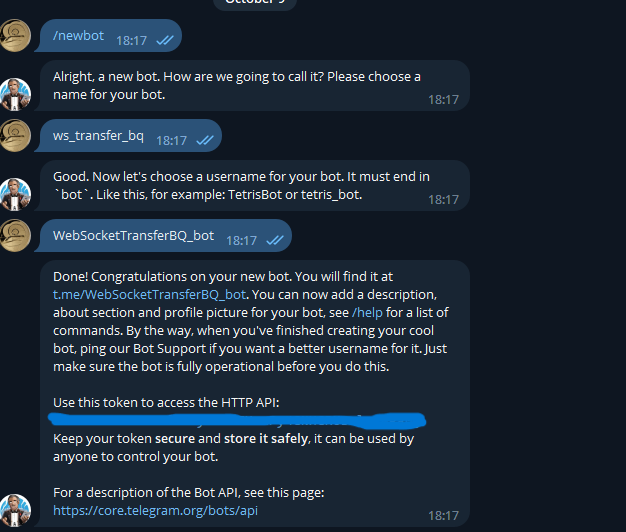
Replace 'tokenn' with your actual bot token.
BOT_TOKEN = 'YOUR_BOT_TOKEN'
You also need to get your API OAuth Token from Bitquery, you can get it for free by creating an account here
Step 3: Define a Function to Send Messages A function named send_message is defined. It takes an update object and a message string as arguments and sends the message to the Telegram chat.
def send_message(update: Update, message: str): update.message.reply_text(message)
Step 4: Define Functions for Handling Long Messages Since the response received from the Bitquery API is much longer than allowed limits( 4000 characters), we will write a function that splits the text and sends it to the chat.
def split_text(text, max_length):
return [text[i:i + max_length] for i in range(0, len(text), max_length)]
def send_long_message(update: Update, long_message, max_message_length=4000):
message_parts = split_text(long_message, max_message_length)
for part in message_parts:
send_message(update, part)
Two functions, split_text and send_long_message, are defined to handle long messages. split_text breaks a long message into smaller parts, and send_long_message sends a long message as multiple smaller messages to avoid Telegram's message length limits.
Step 5: Define WebSocket Code
The my_component function is an asynchronous function that handles the WebSocket connection to Bitquery. You can read more about how to use it here
The below code sends a GraphQL subscription query that listens to server for latest transfers on the Ethereum chain, i.e. it subscribes to the EVM.Transfers event.
async def my_component(update):
url = 'wss://streaming.bitquery.io/graphql'
message = json.dumps({
"type": "start",
"id": "1",
"payload": {
"query": "subscription {\n EVM {\n Transfers {\n Transfer {\n Amount\n __typename\n Currency {\n __typename\n Symbol\n }\n }\n }\n }\n}",
"variables": {}
},
"headers": {
Authorization: "Bearer your_access_token_here",
}
})
async def connect(update):
async with websockets.connect(url, subprotocols=['graphql-ws']) as ws:
await ws.send(message)
while True:
response = await ws.recv()
response = json.loads(response)
if response.get('type') == 'data':
response_text = f"{response['payload']['data']['EVM']['Transfers']}"
send_long_message(update, response_text)
await connect(update)
- It waits for new events.
- When it receives a new event, it sends the event data to the Telegram bot.
Step 6: Start WebSocket and Send Updates to Telegram The start_websocket_and_send_updates function initiates the WebSocket connection defined in my_component. It also handles exceptions if the connection encounters any issues.
async def start_websocket_and_send_updates(update):
try:
await my_component(update)
except Exception as e:
print(str(e))
Step 7: Command Handler to Start WebSocket Connection The start function is a command handler that responds to the /start command on Telegram. It sends a message indicating that it's starting the WebSocket connection and then calls start_websocket_and_send_updates to begin the WebSocket connection.
def start(update: Update, context: CallbackContext):
update.message.reply_text("Starting WebSocket connection...")
asyncio.run(start_websocket_and_send_updates(update))
Step 8: Create and Configure the Telegram Bot In the main function, the Telegram bot is created and configured. It registers the /start command handler. It then starts the bot and waits for updates.
def main():
tracemalloc.start()
updater = Updater(BOT_TOKEN, use_context=True)
dp = updater.dispatcher
dp.add_handler(CommandHandler("start", start))
updater.start_polling()
updater.idle()
**Step 9: Run the Bot** The script checks if it's the main module and starts the bot.
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()