Build Multi-Chain NFT Scanner
In this guide, we will use Bitquery Streaming API for scanning NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) across various blockchains for the given address. We'll explore how to build an NFT scanner that works with a specific wallet address using Python.
Why Bitquery for NFT Scanning?
- Multi-Blockchain Support: Bitquery covers a wide range of blockchains, providing a holistic view of the NFT marketplace.
- Real-Time Data: Access up-to-the-minute information on NFT transactions and holdings.
- Customizable Queries: With GraphQL, tailor your queries to fetch exactly what you need, without unnecessary data overhead.
Using Bitquery IDE for Custom Queries
For a more tailored experience:
- Open Bitquery IDE: Access the IDE in your browser.
- Write and Run Queries: Utilize the IDE to write custom GraphQL queries. For instance, you can modify the earlier NFT balance query to suit other blockchains or different parameters.
- Analyze the Results: Execute your queries and analyze the data returned directly in the IDE.
The following query can be used to display the primary metadata for NFTs on any blockchain. Make sure the schema being used if from (https://streaming.bitquery.io/graphql)
query ($network: evm_network, $limit: Int!, $offset: Int!, $address: String) {
EVM(dataset: combined, network: $network) {
BalanceUpdates(
orderBy: {descendingByField: "amount"}
limit: {offset: $offset, count: $limit}
where: {BalanceUpdate: {Address: {is: $address}}, Currency: {Fungible: false}}
) {
Currency {
Name
Symbol
SmartContract
}
BalanceUpdate {
Address
Id
URI
}
amount: sum(of: BalanceUpdate_Amount)
Block {
Time(maximum: Block_Time)
}
count
ChainId
Transaction {
Hash
}
}
}
}
Below the sections, where we write the query. There is arguments section, where we can input our arguments like network, limit, address, etc. as JSON object.
{
"network": "eth",
"limit": 10,
"offset": 0,
"address": "0x771c82dd5c6e1011adcf4372e77cf5e5587a9054"
}
Now we can use the export code tool to create simple CLI based tools to scan various blockchains for NFTs in any of the languages available in the drop down.
Let’s quickly build a python script for the same to make the data more readable and accessible.
- Install the Requests Library:
The requests library is used to make HTTP requests in Python. Install it using pip:
pip install requests
- Export the code using the export code snippet button on the top right of (https://ide.bitquery.io/).
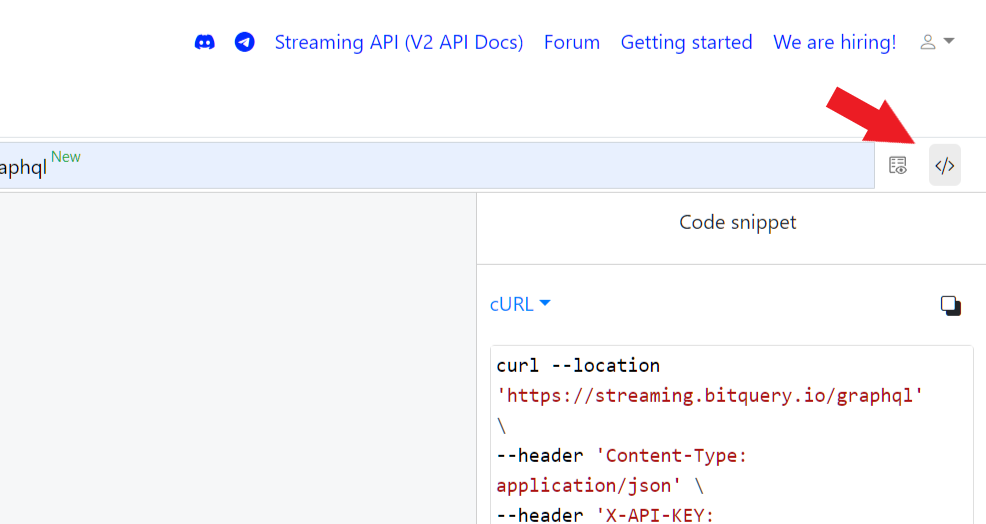
- Modifying for better readability
import requests
import json
def fetch_nft_data(wallet_address, api_key, block_chain):
url = "https://streaming.bitquery.io/graphql"
# GraphQL query payload
payload = json.dumps({
"query": """
query ($network: evm_network, $limit: Int!, $offset: Int!, $address: String) {
EVM(dataset: combined, network: $network) {
BalanceUpdates(
orderBy: {descendingByField: "amount"}
limit: {offset: $offset, count: $limit}
where: {BalanceUpdate: {Address: {is: $address}}, Currency: {Fungible: false}}
) {
Currency {
Name
Symbol
SmartContract
}
BalanceUpdate {
Address
Id
URI
}
amount: sum(of: BalanceUpdate_Amount)
Block {
Time(maximum: Block_Time)
}
count
ChainId
Transaction {
Hash
}
}
}
}
""",
"variables": json.dumps({
"network": block_chain,
"limit": 100,
"offset": 0,
"address": wallet_address
})
})
# API headers
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
Authorization: "Bearer your_access_token_here",
}
# Make the API request
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=payload)
# Parse the JSON response
data = response.json()
# Check if 'data' key is in the response
if 'data' in data:
return data['data']['EVM']['BalanceUpdates']
else:
raise Exception("No data found or error in response")
def main():
api_key = "YOUR_BITQUERY_API_KEY" # Replace with your Bitquery API key
wallet_address = input("Enter Ethereum wallet address: ")
block_chain = input("Enter block chain name(eth, bsc, arbitrum, any evm): ") #see blockchain identifiers in IDE
try:
balance_updates = fetch_nft_data(wallet_address, api_key,block_chain) #default eth
total_nfts = sum(int(item['count']) for item in balance_updates if item['count'])
print(f"Total NFTs in Wallet: {total_nfts}")
has_nfts = "Yes" if total_nfts > 0 else "No"
print(f"Does Wallet Have NFTs? {has_nfts}")
except Exception as e:
print("An error occurred:", str(e))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- Run code in terminal
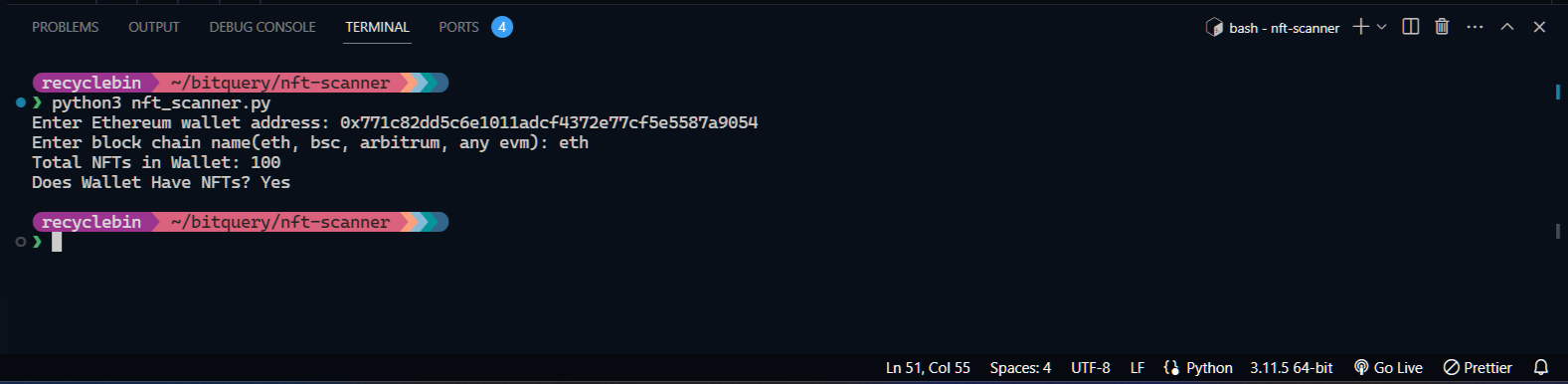
This code displays whether a wallet holds NFT’s on a blockchain and how many it holds. In order to see the specifics of the NFTs held in the wallet the following snippet can be added to view the json dump which we already formatted in the above code.
for item in balance_updates:
# Format and print each item in a human-readable way
print(json.dumps(item, indent=2))
Exploring NFTs Beyond Code: Bitquery Explorer
Bitquery Explorer for Easy Exploration
For those who prefer a GUI over code:
-
Visit Bitquery Explorer (https://explorer.bitquery.io/) : Navigate to the Explorer on your web browser.
-
Select the Blockchain: Choose the blockchain from which you want to fetch NFT data.
-
Input the Wallet Address: Search for the specific wallet address in the provided search bar.
Click on the NFT’s on Address Tab: The Explorer will display NFT transactions and holdings associated with the address, offering a detailed view of the NFT landscape related to that wallet.